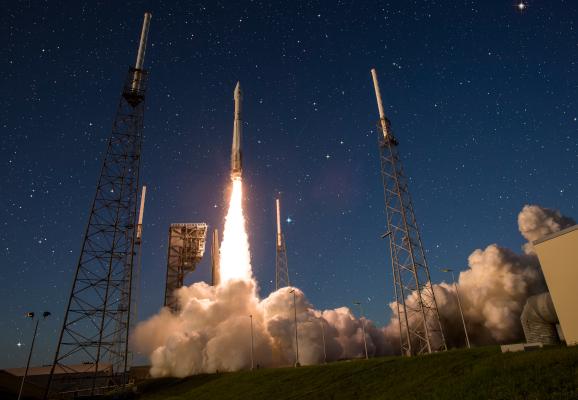
Designing the engines that power rockets, satellites and other spacecraft for launch or flight in space is the work of propulsion engineers.

The Rundown
What does a propulsion engineer do?
Propulsion engineers design, test, and manufacture spacecraft propulsion systems, using scientific and engineering knowledge.
Propulsion engineering is a speciality within aerospace engineering. Propulsion engineers design the engines that provide rockets, missiles, satellites and other spacecraft with the means to accelerate for launch or flight in space. A number of different propulsion technologies are in use today, including chemical propulsion and electromagnetic propulsion. Researchers are also looking into new ways of propelling spacecraft that are more sustainable or that have the potential to help spacecraft travel further distances than ever before.
What you’ll need to know and do
Because most forms of propulsion involve a chemical source of fuel, propulsion engineers need to have a strong grasp of chemistry. They also need strong mechanical skills in order to successfully design or modify the moving parts of an engine. Propulsion engineers are often senior engineers with several years of experience in another area. They typically work in a team with mechanical engineers and other technical specialists.
Your study pathway
The minimum study requirement to work as a propulsion engineer is an undergraduate degree in aerospace engineering. Some employers may have further requirements, such as postgraduate qualifications or research in a particular speciality.
Almost all universities in Australia offer degrees in engineering. Visit individual university websites for more information.
Postgraduate qualifications by coursework or research in relevant areas of engineering may also support a career in propulsion engineering. Visit individual university websites for more information.
